先说结论:
-
ctx.close():只会总当前处理器BHandler出发,向前寻找出站Handler,并调用它们的close()方法;
-
ctx.channel().close():将从整个pipeline的tail尾部向前寻找所有的出站Handler,并调用它们的close()方法!
一、编写测试代码:
1、需要引入的依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>io.netty</groupId> <artifactId>netty-all</artifactId> <version>4.1.70.Final</version> </dependency>
2、编写一个双向处理器ZidanHandler:
/**
* ChannelDuplexHandler:双向处理器:
* 既继承了ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter类,
* 又实现了ChannelOutboundHandler接口。
* @Author jiguiquan
* @Email jiguiquan@haier.com
* @Data 2023-07-12 9:31
*/
public class ZidanHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(ctx.name() + " channelRead: " + msg);
String result = (String) msg;
if (("ctx.close." + ctx.name()).equals(result)) {
ctx.close();
} else if (("ctx.channel.close." + ctx.name()).equals(result)) {
ctx.channel().close();
} else {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}
@Override
public void close(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println(ctx.name() + " close");
ctx.close(promise);
}
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println(ctx.name() + " write");
ctx.write(String.format("[%s]%s", ctx.name(), msg), promise);
}
}
3、主入口类NettyServer:
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup(3);
new ServerBootstrap()
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.group(boss, worker)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline()
.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder())
.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder())
.addLast("A", new ZidanHandler())
.addLast("B", new ZidanHandler())
.addLast("C", new ZidanHandler());
}
}).bind(8090).sync();
}
}
二、启动项目,进行测试看现象
1、项目启动后,我们使用本地的telnet命令作为客户端进行交互:
C:\Users\admin>telnet localhost 8090 # 重点,进入telnet窗口后,我们需要按下 Ctrl + ]键 欢迎使用 Microsoft Telnet Client Escape 字符为 'CTRL+]' Microsoft Telnet>
2、我们先用telnet发送“ctx.close.B”字符串:
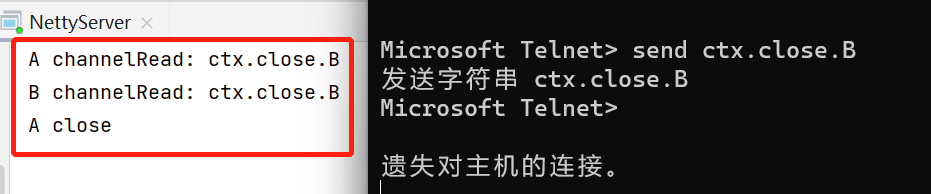
3、我们再用telnet发送“ctx.channel.close.B”字符串:
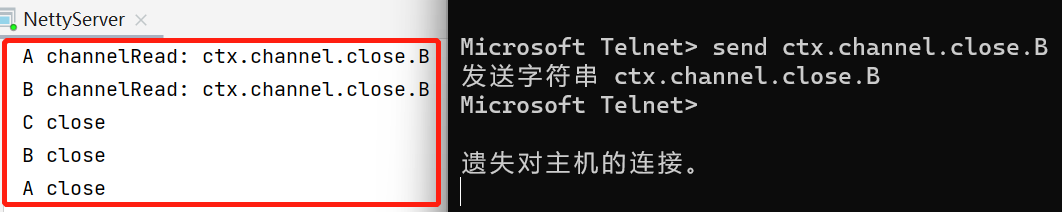
4、根据现象得出结论:
-
ctx.close():只会总当前处理器BHandler出发,向前寻找出站Handler,并调用它们的close()方法;
-
ctx.channel().close():将从整个pipeline的tail尾部向前寻找所有的出站Handler,并调用它们的close()方法!
三、通过源码弄明白为什么
1、ctx.close() 的源码:
abstract class AbstractChannelHandlerContext implements ChannelHandlerContext, ResourceLeakHint {
public ChannelFuture close() {
return this.close(this.newPromise());
}
public ChannelFuture close(final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (this.isNotValidPromise(promise, false)) {
return promise;
} else {
// 获取下一个出站Handler(出站是向前,所以实际是前一个)
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = this.findContextOutbound(4096);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
next.invokeClose(promise);
} else {
safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {
public void run() {
next.invokeClose(promise);
}
}, promise, (Object)null, false);
}
return promise;
}
}
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextOutbound(int mask) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
EventExecutor currentExecutor = this.executor();
do {
// 找出当前handlerContext的prev前一个handlerContext
// 但是会跳过不是Outbound的那些handler
ctx = ctx.prev;
} while(skipContext(ctx, currentExecutor, mask, 130560));
return ctx;
}
}
2、ctx.channel().close() 的源码:
public abstract class AbstractChannel extends DefaultAttributeMap implements Channel {
public ChannelFuture close() {
return this.pipeline.close();
}
public final ChannelFuture close() {
// 其实到这里已经很清晰了,从当前整个pipeline中的tail尾节点开始,向前寻找出站handler,
// 并执行他们的close()方法
return this.tail.close();
}
}
四、总结:
1、那么我们何时使用ctx.close(),又何时使用ctx.channel().close()方法呢:
-
如果你正写一个 ChannelHandler, 并且在处理逻辑时,想在这个 handler 中关闭 channel, 则直接调用 ctx.close();
-
如果你正准备从一个外部的 handler (例如, 你有一个后台的非I/O线程, 并且你想从该线程中关闭连接),那么就可以调用ctx.Channel.close());
但是这种规则也是非绝对的!
2、其他类似的方法对:
-
ctx.write() 与 ctx.channel().write()
-
ctx.writeAndFlush() 与 ctx.channel().writeAndFlush()